Heart is the organ system in the main kardiovaskuler. Heart was established by a muscular organs, and the Apex cordis base, left and right atrium and right and left ventrikel. Heart size is approximately 12 cm long, 8-9 cm wide thick seta approximately 6 cm.
Heavy heart about 7-15 oz or 200 to 425 grams and a little more than the fist. Every day the heart rattle and 100,000 times in the period of the heart pumping 2000 gallons of blood, equivalent to 7571 liters of blood.
The position was located the heart of both tuberculosis and chest are in the middle, on the diaphragma thoracis and located approximately 5 cm above processus xiphoideus.
On the right edge is located at the cranial edge cranialis pars cartilaginis Costa dextra III, 1 cm lateral edge of the sternum. On the right edge is located at the caudal edge cranialis pars VI cartilaginis Costa dextra, 1 cm lateral edge of the sternum
The left edge are the heart of the cranial edge caudal pars II cartilaginis Costa Sinistra sternum in the lateral edge, the edge is on the left caudal space intercostalis 5, approximately 9 cm in the left linea medioclavicularis.
Membrane that envelop the heart called the pericardium which consists of fibrosa layer and serosa, in the cavum pericardii containing 50 cc that functions as a lubricant so that there is no friction between the pericardium and epicardium. Epicardium is the outermost layer of the heart, the next layer is the layer miokardium where this layer is the layer thick. Last layer is a layer of endocardium.
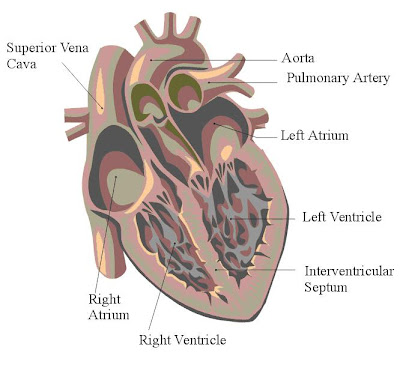
There are 4 rooms in the heart where two of the space is called the atrium and the rest is ventrikel. At the cloud known as the atrium and foyer with closet ventrikel known.
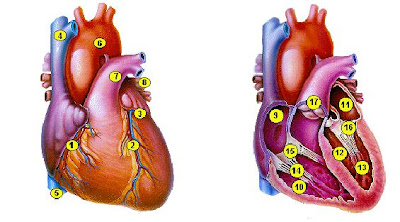 1. Right Coronary
1. Right Coronary2. Left Anterior Descending
3. Left Circumflex
4. Superior Vena Cava
5. Inferior Vena Cava
6. Aorta
7. Pulmonary artery
8. Pulmonary vein
9. Right Atrium
10. Right Ventricle
11. Left Atrium
12. Left Ventricle
13. Papillary Muscles
14. Chordae Tendineae
15. Tricuspid Valve
16. Mitral Valve
17. ValveFungsi main pulmonary heart is pumping darh to the entire body where at the time of the heart muscle-pumping heart muscle (miokardium) that move. In addition, heart muscle also has the ability to cause electrical stimulus.
Second is the atrium space with a thin wall of muscle because of the low pressure caused by the atrium. Instead ventrikel have a thick wall of muscle, especially ventrikel that have left three more layers of thick ventrikel right.
Activities contraction heart pumping blood to the body overlooks always started by the electrical activity. Electrical activity started in nodus sinoatrial (SA nodus), which is located in the cleft between the vena Cava suiperior and right atrium. Nodus SA on the waves so depolarisasi spontaneously evoke action potential spread through the muscle cells atrium, nodus atrioventrikuler (nodus AV), the His, Purkinje fiber, and finally to the whole muscle ventrikel.
 Therefore, the heart does not have to do the rest for the contraction to meet the needs of the body, the heart requires more blood than other organs. The flow of blood to the heart from the coronary arterial-right and left. Both coronary arterial out of the aorta is approximately ½ inch above aorta valve and running on the surface of the pericardium. Then arteriol and a fork in the capillary walls ventrikel. Occurred after the exchange of O2 and CO2 in the capillary, the flow of ventrikel taken from the vena through vena coronary and straight into the right atrium where the flow of blood from the vena whole body will be empty.
Therefore, the heart does not have to do the rest for the contraction to meet the needs of the body, the heart requires more blood than other organs. The flow of blood to the heart from the coronary arterial-right and left. Both coronary arterial out of the aorta is approximately ½ inch above aorta valve and running on the surface of the pericardium. Then arteriol and a fork in the capillary walls ventrikel. Occurred after the exchange of O2 and CO2 in the capillary, the flow of ventrikel taken from the vena through vena coronary and straight into the right atrium where the flow of blood from the vena whole body will be empty.Ditubuh circulation of blood circulation there are 2 that tuberculosis and systemic circulation. Circulation tuberculosis ventrikel right from the start to the arterial pulmonalis, large and small arterial, capillary go to tuberculosis, after a paru's exit through a small vena, vena pulmonalis and finally back to the left atrium. Circulation has low pressure that is approximately 15-20 mmHg in the arterial pulmonalis.
Systemic circulation starting from the aorta to the left ventrikel ago major arterial, minor arterial, arteriole and to the entire body and to venule, a small vena, vena large, inferior vena Cava, superior vena Cava eventually return to the right atrium.

Systemic circulation has a special function as a source of pressure that tinggindan carry oxygen to the network that need. In the capillary terjadin exchange O2 and CO2 on the systemic circulation of O2 and CO2 go out in the capillary circulation in tuberculosis O2 entry and exit from the capillary CO2.
Volume of each component in the blood circulation is different. 84% of the volume of blood in the body found in the systemic circulation, where 64% in vena, 13% in the arterial and 7% in arteriol and capillary.







No comments:
Post a Comment